Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Takahashi, Osamu*; Shibui, Yohei*; Xu, P. G.; Harjo, S.; Suzuki, Tetsuya*; Tomota, Yo*
Quantum Beam Science (Internet), 4(1), p.16_1 - 16_15, 2020/03
Hojo, Kiminobu*; Hayashi, Shotaro*; Nishi, Wataru*; Kamaya, Masayuki*; Katsuyama, Jinya; Masaki, Koichi*; Nagai, Masaki*; Okamoto, Toshiki*; Takada, Yasukazu*; Yoshimura, Shinobu*
Mechanical Engineering Journal (Internet), 3(4), p.16-00083_1 - 16-00083_16, 2016/08
Performance demonstration certification of non-destructive inspection for cast stainless steel (CASS) has been planned but the target flaw depth to be detected has not been determined yet in Japan. The target flaw size is closely connected to the allowable flaw size which is determined by flaw evaluation of the rules on fitness-for-service. For rational mitigation of the acceptable flaw size, application of probabilistic fracture mechanics (PFM) is one of the useful countermeasures compared with deterministic approach. In this paper, benchmark problems for a CASS pipe were proposed with intention applying and verifying PFM codes. As the fracture modes, fatigue crack extension, plastic collapse and ductile crack initiation were assumed. Six organizations participated in the benchmark analysis and failure probabilities from them were compared. As a result the failure probability of each problem showed good agreement and the code for application of CASS issue has been verified.
Kaji, Yoshiyuki; Miwa, Yukio; Tsukada, Takashi
Nihon Kikai Gakkai M&M 2005 Zairyo Rikigaku Kanfarensu Koen Rombunshu, p.175 - 176, 2005/12
From results of analysis of plastic deformation behavior at SCC crack tip by EBSP method, the conclusions was obtained as follows: (1)Regarding to basic data for quantitative evaluation of plastic deformation behavior at SCC crack tip, we obtained relationship between plastic deformation and misorientation of grain using SSRT result for SUS316L stainless steel in high temperature water and local plastic strain was able to estimate using this relationship. (2)From experimental results of plastic strain at SCC crack and ductile crack tips using relationship between misorientation and plastic deformation, plastic strain near ductile crack tip was larger than that at SCC crack tip. Plastic deformation region was, however, corresponded to region of about one grain at crack tip for both SCC and ductile cracks.
 -TiAl intermetallic compounds
-TiAl intermetallic compoundsSawai, Tomotsugu; Hishinuma, Akimichi
Journal of Physics and Chemistry of Solids, 66(2-4), p.335 - 338, 2005/02
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:49.98(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)TiAl intermetallic compounds are potential materials for high temperature structural applications. They have also low induced radio-activity and good radiation resistance, which make these alloys very attractive in nuclear applications. Their ductility at low temperatures should be, however, still improved and their deformation mechanism is of great concern. In this study, intersections of deformation twins in  -TiAl grains were examined in Ti-47at%Al alloy specimens tensile-tested at 873 K. Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) revealed 1/2
-TiAl grains were examined in Ti-47at%Al alloy specimens tensile-tested at 873 K. Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) revealed 1/2 110]{111} ordinary-type dislocations and 1/6
110]{111} ordinary-type dislocations and 1/6 112]{111} twins in deformed
112]{111} twins in deformed  -TiAl grains. Some
-TiAl grains. Some  -TiAl grains contained twins on two different {111} planes, which intersect along
-TiAl grains contained twins on two different {111} planes, which intersect along  110] directions (type-1). No twin intersection along
110] directions (type-1). No twin intersection along  101] (type-2) was observed, which was often reported in compressed specimens. Results are discussed with the Schmid factor distributions of twinning systems and ordinary slip systems as the function of tensile directions.
101] (type-2) was observed, which was often reported in compressed specimens. Results are discussed with the Schmid factor distributions of twinning systems and ordinary slip systems as the function of tensile directions.
Igawa, Naoki; Taguchi, Tomitsugu; Yamada, Reiji; Ishii, Yoshinobu; Jitsukawa, Shiro
Ceramic Engineering and Science Proceedings, Vol.26, No.2, p.27 - 34, 2005/00
no abstracts in English
Ishiyama, Shintaro; Buchkremer, H. P.*; St ver, D.*
ver, D.*
Nihon Kinzoku Gakkai-Shi, 68(9), p.831 - 837, 2004/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Metallurgy & Metallurgical Engineering)NiAl intermetallics with dispersive Cr particles consolidated by the Hot Isostaic Press(HIP) and Reactive HIP(RHIP) techniques, has been investigated. Mechanical properties of HIPed and RHIPed materials with various Cr concentrations ranging form 0 to 30 mass.%Cr, were examined at various temperatures. The consolidation temperature of RHIP materials decreases with Cr addition; when RHIPing NiAl+xCr compounds with 25 mass% has attained, remarkable high ductility over 17% elongation and over 400MPa tensile strength at 873K. A very high tensile strength of HIPed NiAl+20wt.%Cr about 600MPa with 10% elongation was achieved at 873K.
Tanigawa, Hiroyasu; Hashimoto, Naoyuki*; Sakasegawa, Hideo*; Klueh, R. L.*; Sokolov, M. A.*; Shiba, Kiyoyuki; Jitsukawa, Shiro; Koyama, Akira*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 329-333(1), p.283 - 288, 2004/08
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:75.21(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Reduced-activation ferritic/martensitic steels (RAFs) were developed as candidate structural materials for fusion power plants. In a previous study, it was reported that ORNL9Cr-2WVTa and JLF-1 (Fe-9Cr-2W-V-Ta-N) steels showed smaller ductile-brittle transition temperature (DBTT) shifts compared to IEA modified F82H (Fe-8Cr-2W-V-Ta) after neutron irradiation up to 5 dpa at 573K. This difference in DBTT shift could not be interpreted as an effect of irradiation hardening, and it is also hard to be convinced that this difference was simply due to a Cr concentration difference. To clarify the mechanisms of the difference in Charpy impact property between these steels, various microstructure analyses were performed.
Tanigawa, Hiroyasu; Hashimoto, Naoyuki*; Sokolov, M. A.*; Klueh, R. L.*; Ando, Masami
Fusion Materials Semiannual Progress Report for the Period Ending (DOE/ER-0313/35), p.58 - 60, 2004/04
1TCT fracture toughness specimens of F82H-IEA steel were fatigue precracked and sliced in specimen thickness wise for microstructure analysis around the precrack. The microstructure around the precrack was observed by optical microscopy (OM), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), orientation imaging microscopy (OIM), and transmission electron microscopy (TEM). TEM samples around the crack front were prepared by focused ion beam (FIB) processor. The fracture surfaces of tested 1TCT specimens were also observed. OM observation showed that the precrack penetration was straight in the beginning, and then tended to follow a prior austenite grain boundary and to branch into 2 to 3 directions at the terminal. SEM and OIM observations revealed that the both microstructures around the precracks and ahead of the precrack had turned into cell structure, which is the typical microstructure of fatigue-loaded F82H. TEM images and inverse pole figures obtained from the crack-front region confirmed this structure change.
 Ti/(Be) and Be
Ti/(Be) and Be V/(Be) two-phase alloys
V/(Be) two-phase alloysMishima, Yoshinao*; Yamamoto, Keisuke*; Kimura, Yoshisato*; Uchida, Munenori*; Kawamura, Hiroshi
JAERI-Conf 2004-006, p.184 - 189, 2004/03
no abstracts in English
Uchida, Munenori*; Kawamura, Hiroshi; Uda, Minoru*; Ito, Yoshio*
Fusion Engineering and Design, 69(1-4), p.491 - 498, 2003/09
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:69.06(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Li, Y.*; Kato, Daisuke*; Shibata, Katsuyuki; Onizawa, Kunio
Nihon Kikai Gakkai Rombunshu, A, 69(678), p.239 - 245, 2003/02
no abstracts in English
Naoe, Takashi*; Futakawa, Masatoshi; Wakui, Takashi*; Kogawa, Hiroyuki
Nihon Kikai Gakkai Kanto Shibu Ibaraki Koenkai (2002) Koen Rombunshu, p.3 - 4, 2002/09
no abstracts in English
Shibata, Katsuyuki; Onizawa, Kunio; Kato, Daisuke*; Li, Y.*
Nihon Kikai Gakkai 2001-Nendo Nenji Taikai Koen Rombunshu, p.389 - 390, 2001/00
no abstracts in English
Kato, Daisuke*; Li, Y.*; Shibata, Katsuyuki; Onizawa, Kunio
Nihon Kikai Gakkai 2001-Nendo Nenji Taikai Koen Rombunshu, p.391 - 392, 2001/00
no abstracts in English
Ishii, Toshimitsu; Omi, Masao; Saito, Junichi; Hoshiya, Taiji; Ooka, Norikazu; Jitsukawa, Shiro; Eto, Motokuni
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 283-287(Part.2), p.1023 - 1027, 2000/12
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:62.16(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Fujita, Mitsutane*; Kinugawa, Junichi*; Tsuji, Hirokazu; Kaji, Yoshiyuki; Tachi, Yoshiaki*; Saito, Junichi*; Shimura, Kazuki*; Nakajima, Ritsuko*; Iwata, Shuichi*
Fusion Engineering and Design, 51-52, p.769 - 774, 2000/11
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:12.1(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Nishiyama, Yutaka; Onizawa, Kunio; Idei, Yoshio; Suzuki, Masahide
JAERI-Research 2000-047, 32 Pages, 2000/10
no abstracts in English
;
JNC TN9400 2000-035, 164 Pages, 2000/03
High Strength Ferritic/Martensitic Steel (PNC-FMS : 0.12C-11Cr-0,5Mo-2W-0.2V-0.05Nb), developed by JNC, is one of the candidate materials for the long-life core of large-scale fast breeder reactor. Ductile brittle transition temperature (DBTT) was tentatively determined in 1992 in material design base standard of PNC-FMS. Howevcr, specimen size effect on impact property and upper shelf energy (USE) have not been evaluated. ln this study, effects of specimen size, thermal aging and neutron irradiation on the charpy impact property of PNC-FMS were evaluated, using together with recently obtained data. The design value of USE and DBTT as fabricated and each correlation of aging and irradiation effects were determined. The results are summarized as follows. (1)lt was found that USE is related to (Bb) as USE=m(Bb)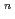 , where B is specimen width, b is ligament size and both m and n are constant. For PNC-FMS, n value is equal to 1.4. It's possible to determine n value from USE (J) for full size specimen using the correlation: n=1.38
, where B is specimen width, b is ligament size and both m and n are constant. For PNC-FMS, n value is equal to 1.4. It's possible to determine n value from USE (J) for full size specimen using the correlation: n=1.38 10
10 USE + 1.20. (2)lt was clarified that DBTT is correlated with (BKt) as DBTT=p(log
USE + 1.20. (2)lt was clarified that DBTT is correlated with (BKt) as DBTT=p(log BKt)+q, where Kt is elastic stress concentration factor and both p and q are constant. For PNC-FMS, the correlation is as follows: DBTT=119(log
BKt)+q, where Kt is elastic stress concentration factor and both p and q are constant. For PNC-FMS, the correlation is as follows: DBTT=119(log BKt)-160. (3)DBTT estimated at the irradiation temperature from 350 to 650
BKt)-160. (3)DBTT estimated at the irradiation temperature from 350 to 650  C for sub size specimen (width and height are 3 and 10 mm, respectively), was below 180
C for sub size specimen (width and height are 3 and 10 mm, respectively), was below 180  C, based on the design value of DBTT as fabricated and each correlation of aging and irradiation effects.
C, based on the design value of DBTT as fabricated and each correlation of aging and irradiation effects.
Hishinuma, Akimichi; Tabuchi, Masayuki; Sawai, Tomotsugu
Intermetallics, 7(8), p.875 - 879, 1999/00
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:59.64(Chemistry, Physical)no abstracts in English
Watanabe, Katsutoshi; Hishinuma, Akimichi; *; *
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 258-263, p.848 - 852, 1998/00
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:63.67(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English